Theme: Promising future of Bioenergy and Biofuels
Bioenergy Meet 2020
We cordially welcome all the participants from all part of the world to attend the scientific event entitled “11th Annual Congress on Bioenergy and Biofuels” scheduled during April 20-21, 2020 in Amsterdam, Netherlands.
Bioenergy Meet 2020 is the leading conference dedicated to Bioenergy, Renewable Energy and Biofuels researchers with the theme “Devising a Sustainable Bioeconomy”
The goal of Bioenergy Meet 2020 is to deliver an outstanding program for exchange of ideas and authoritative views by leading scientists which covers the entire spectrum of research in Biofuels and Bioenergy and share the cross-cultural experiences of various production procedures.
Why attend?
We strive to make Bioenergy Meet 2020 a success, with your support and high-quality talks from both Bioenergy as well as Biofuels committees and professionals. During the conference, we assure you that you will experience world class facilities and hospitality at the conference.
Fuel for transport makes up almost a third of the current world energy consumption. Biofuels – has emerged as one of many possible alternatives to fossil fuels. Bioenergy is one of the many diverse resources available to help meet our demand for energy. Bioenergy use falls into 2 main categories: “traditional” and “modern”. Traditional use refers to the combustion of biomass in such forms as wood, animal waste, and charcoal. Modern bioenergy technologies embody liquid biofuels made from pulp and different plants; bio-refineries; biogas made through anaerobic digestion of residues; wood pellet heating systems. By 2030, 1 billion tons of biomass could produce up to 50 billion gallons of biofuels; produce 50 billion pounds of biobased chemicals and bioproducts; generate 85 billion kilowatt-hours of electricity to power 7 million households; contribute 1.1 million jobs to the economy, and keep $260 billion in the United States
Target Audience
Bioenergy Meet 2020 is expecting the participants from all over the globe in various fields. This combination of the audience will give an ideal blend to justify our theme “Devising a Sustainable Bioeconomy”
Bioenergy Meet 2020 expecting attendees from,
- Fuel Engineers
- Chemical Engineers
- Professors, Researchers, Students and Technical Staff from the field of Chemical Engineering
- Engineers and Delegates from Aviation and Automobile companies
- Directors/Co-Directors of Research-based companies across Europe and US who are investing in Biofuels and Bioenergy
Track 01: Feedstock and Resources for Biofuels and Biorefinery
A feedstock is characterized as any sustainable, organic material that can be utilized straightforwardly as a fuel, or changed over to another type of fuel or vitality item. Biomass feedstocks are the plant and algal materials used to determine fills like ethanol, butane, biodiesel, and other hydrocarbon fuels. A feedstock is characterized as an inexhaustible, natural material that can be reutilized straightforwardly as a fuel, or changed over to another type of fuel or vitality item. Cases of biomass feedstock’s incorporate corn starch, sugarcane juice, trim build-ups, for example, corn stover and sugarcane bagasse, reason developed grass harvests and woody plants.
Track 02: Biomass for Energy
Biomass is an energy that comes from plants and animals and it is a source of energy. It contains stored energy from the sun and it is called photosynthesis Solid biomass, such as wood and garbage, can be burned directly to produce heat. Biomass can also be converted into a gas called biogas or into liquid biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel. These fuels can then be burned for energy. Ethanol is made from crops such as corn and sugar cane that are fermented to produce fuel ethanol for use in vehicles. Biodiesel is produced from vegetable oils and animal fats and can be used in vehicles and as heating oil. Although the biomass industry will be expensive it can be a very big step in protecting the resources in the world and reducing greenhouse gases that affect the environment greatly. Even though the biomass industry will be releasing emissions into the atmosphere, but will be much less than any other industry as the innovation will be using the emissions also to produce
Track 03: Forestry as Carbon Sink
Plants are categorized as Autotrophs, meaning they have the ability to produce their own energy source by utilizing the natural elements like sunlight, water and so on, through the longest chemical reaction found in nature, photosynthesis. Plants produce glucose, which is a carbon-based biomolecule. Carbon in glucose is gained from carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, which is considered one of the major greenhouse gases, contributing to Global climate change. Plants are also carbon sources and they release stored carbon back into the environment in events such as a forest fire. However, the release of carbon is minute compared to carbon absorption. Therefore, Forests act as “carbon sinks” which will reduce carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere. Reforestation is one such controllable solution for reducing carbon footprint and preventing increasing global temperatures.
Track 04: Environmental Impacts of Bioenergy Sector
Burning either fossil fuels or biomass releases carbon dioxide a greenhouse gas. Anyhow, the plants that are the source of biomass capture a nearly equivalent amount of CO2 through photosynthesis while they are growing, which can make biomass a carbon-neutral energy source. One of the major motives for producing biofuels is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and to mitigate the outcomes of global warming produced through fossil fuels. But, according to the food and Agriculture Organization of the UN, a few unintended effects of biofuel manufacturing are on land, water, and biodiversity
Track 05: Bioalcohols
Bioalcohols are produced by the microbial action and enzyme activity by fermentation of sugars, cellulose, and starch. At first, bioalcohol were produced by using unused parts of edible crops as feedstock, this was termed as the first generation of bioalcohol. The second generation of bioalcohols are synthesized from non - consumable crops, therefore they avoid competition with the food sector, but also create conflict for land usage. The second generation of bioalcohols is synthesized to be more efficient and cost-effective than the first generation.
The use of an alcohol as fuels is a new concept but the value of alcohol for drinking made it more expensive for use as a fuel than the newly discovered petroleum. Ethanol is the standard drinking alcohol and it is not poisoning we are very off to start with the methanol for the time being, alcohol powers won't supplant hydrocarbon fills. They will, in any case, be vital added substances to powers for a long time to come. In the event that science keeps on advancing and the issue of trading off the natural way of life can be comprehended, at that point liquor fills may give a great other option to petroleum products that enable us to better adjust how much carbon dioxide we put into the climate with how much plants expel.
Track 06: Biodiesel
Biodiesel is produced from biomass as feedstock; therefore this type of fuel is renewable. It is typically used as a blend in regular diesel. Feedstock for biodiesel includes soya bean oil, canola oil, corn oil and even animal fats, many of these sources being recycled from restaurants. Combustion of Biodiesel produces fewer amounts of pollutants such as carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrocarbons and toxic fumes compared to petroleum-based fuel. The US Government says that Biodiesel is carbon-neutral due to the fact that, the carbon dioxide emissions from burning biodiesel can be reabsorbed by the plants grown to provide feedstock for biodiesel production. Biodiesel can be produced from various techniques; recycled vegetable oil can be converted to biodiesel through the process of trans-Esterification which utilizes an acid or a base to accelerate the process. However, the most common method to produce Biodiesel is by the reaction of vegetable oil with methanol in the presence of sodium hydroxide. Using methanol is a cost-effective alternative. Biodiesel from yellow grease is the closest to petroleum-based diesel. Perhaps, the largest market for biodiesel probably will be as a fuel additive, because EPACT requirements are unlikely to increase significantly over the next 20 years. Biodiesel may also be marketed for applications in which reducing emissions of particulates and unburned hydrocarbons are paramount, such as school and transit buses. Because additives improve diesel fuel performance and therefore, are more expensive than diesel fuel, the cost disadvantage for biodiesel would not be as great in the additive market.
Track 07: Biogas
Biogas is a gaseous renewable fuel similar to natural gas. Natural gas is formed alongside fossil fuel by the geological process over millions of years from decomposing organic matter whereas Biogas is formed by anaerobic digestion of organic waste by bacteria. Biogas is primarily composed of methane, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and minute amounts of nitrogen and hydrogen. Animal waste and landfill waste serve as a source of biogas, which is produced in anaerobic digesters. Methane is the primary flammable component of Biogas; it is also an excellent greenhouse gas, which is 21 times greater than carbon dioxide. Therefore, collecting this gas from the landfills and other dumping sites is beneficiary to the environment. Household anaerobic digesters are used in countries such as Africa and China for lighting and cooking in rural areas. Large-scale digesters are utilized to produce biogas on a commercial scale. These digesters use manure slurry from farm animals. Therefore, are typically located adjacent to large animal farms. Another source of biogas production are landfills, where the Biogas is accumulated within the soil covered waste within a period of one year and can be extracted using a series of interconnected pipelines. The gas collected can be channeled to a furnace or a thermal power plant to generate steam and electricity via a steam turbine. Collection of Biogas from landfills reduces chances of explosions within the landfill and also prevents the leakage of greenhouse effect causing methane into the environment
Track 08: Biomass Production and Processing
The burning process generates heat that transformed into energy. The advantage of biomass combustion is that you can use the heat without needing to convert it into another form of energy such as electricity is a sustainable source of fuel to produce energy since, squander buildups will dependably exist – as far as scrap wood, process residuals, and backwoods assets; and. appropriately oversaw backwoods will dependably have more trees, and we will dependably have crops and the leftover natural issue from those harvests. The advantage of biomass combustion is that you can use the heat without needing to convert it into another form of energy such as electricity. You simply use the heat directly for such things as heating your home and heating the water in your home. In addition, the combustion heat can be used for direct heat in plants, manufacturing facilities, and even office buildings. Direct heat can also be converted into electricity.
Track 09: Advanced Biofuels
Advanced biofuels are also termed as the second generation of biofuels. This variation of biofuel is produced from biomass containing, lignin, hemicellulose, and cellulose, pectin, all of which is available from agricultural, forest waste or non-food plants grown specifically grown for biofuel production. Crops for second generation biofuel are aimed to provide more fuel per unit of land and also require less energy to grow and harvest, these crops are called as energy crops. Therefore, this generation is about efficient biofuel production. Advanced biofuels also have more technical properties than previous generation biofuels and are suitable to for synthesizing biopetroleum, biojet fuel, and biobutanol. In a market report conducted, advanced biofuels production facilities worldwide have a cumulative production capacity of 2,530,000 tons per year in 2012. This sector has the potential to grow and solve our current problems with fossil fuel usage and also create several job opportunities.
Track 10: Biofuels and Renewable Energy Sector
A biofuel is created through contemporary organic procedures, for example, farming and anaerobic assimilation, as opposed to a fuel delivered by geographical procedures, for example, those involved with the arrangement of non-renewable energy sources, for example, coal and oil, from an ancient natural issue. Biomass is considered a renewable energy source because its inherent energy comes from the sun and because it can regrow in a relatively short time. Trees take in carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and convert it into biomass and when they die, it is released back into the atmosphere
Track 11: Drop-in Biofuels, Bio hydrocarbons
These biofuels are produced by oilseeds via trans-esterification existing biofuels are Existing biofuels – bioethanol and biodiesel – there is a wide range variation from the fossil fuels in their blend wall properties. There is a high oxygen content hydrophilicity, energy density mainly compatibility in existing engine and infrastructures there are advantages like reduced sulphur oxide emissions by ultra-low sulphur content, reduced hydrocarbons, and nitrogen oxide emissions and it is a low aromatic content Thermochemical methods adopted for biomass are pyrolysis and gasification zero oxygen and sulphur content mark major challenges for production of drop-in fuels from conventional biomass. This demands high hydrogen input on the conventional biomass through crucial ambiguities existing on future of alternative fuels, drop-in fuel has a substantial potential to repute itself as an efficient sustainable eco-friendly fuel in the near future.
Track 12: Biorefinery
A biorefinery is a facility that integrates biomass conversion processes and equipment to produce fuels. The biorefinery concept is analogous to today's petroleum refinery, which produces multiple fuels and products from petroleum. Biorefinery is a facility that integrates biomass conversion processes and gadget to provide fuels, power, and cost-introduced chemical substances from biomass. Biorefinery has similarities to today’s petroleum refinery, which produces a couple of fuels and merchandise from petroleum. With the aid of producing numerous products, a biorefinery takes benefit of the various additives in biomass and their intermediates, consequently maximizing the value derived from the biomass feedstock.
Track 13: Food vs. Fuels Debate
Being a growing population will need more food. The production of biofuels will drive farmers to take fewer food crops. The biofuel concern corn, the source is virtually ethanol the global population maintains to develop, in locations at an alarming fee, and would want to be fed and will count on to stay a progressed lifestyles style, eating more strength inside a long time, crop yields are growing year-on-year. But, decrease than anticipated yields in any given 12 months tend to growth international grain costs, as came about in 2012 in part because of terrible climate and drought affecting the Russian and United States harvest respectively. The consequences of yield versions may be exacerbated via speculation in agricultural commodities. In turn, this can make a contribution to quick-term spikes in meals charges
Track 14: Biofuels Market and Future
Biofuel is economically very important and vegetable used as a raw material for both food and non-food products the center East and Africa constitute an excess capacity for biofuels in future. Enhancing economic activity is expected to boost the biofuels market within the place. Also, exponential consumption of electricity inside the area due to urbanization and consistent infrastructure development has caused heavy dependence on fossil fuels driving the boom of the biofuels market in close to destiny.
The "11th Annual Conference on Bioenergy and Biofuels" April 20-21, 2020 Amsterdam, Netherlands, the event unifies the aim of “Devising a Sustainable Bio-economy" and assimilates 14 scientific sessions bestows worthy discussions on Chemical Engineering, Bioenergy, Biofuels, Biogas. The sensible sessions aid enchanting strategies in the fields of Bioenergy and Biofuels. Bioenergy is one of the prominent resources available to support our demand for energy sources. Bio-mass energy is derived in a significant amount of primary energy from biomass in countries like Finland 18%, Sweden 16% and Austria 13%, USA 4%.
Bioenergy Netherlands:
Bioenergy is obtained from biomass for the production of electricity and heat, or to produce liquid fuels for the purpose of transport. It is available in many forms such as agricultural products, forestry products, and other waste. On the advancement of the utilization of energy from renewable sources, the proportion of biofuels in transport should increase to at least 10% in various regions by end of 2020. In Netherlands, the objective is set at 20%, and it is evaluated this can be delivered altogether in local industries, as long as the activities officially in progress will be effective and extra mechanical scale biofuel plants would be constructed. The review on the condition of projects is in progress in Netherlands and outlines current research activity in advancing waste and by-product based biofuels.
Between 2000 and 2013, fuel ethanol, biodiesel, and hydrogenated vegetable oil yield increased from 17.7 to 116.5 billion liters. This exceptional increment has been driven by administrative interventions
Characteristics of the energy sector in Netherlands
- versatile structure of energy production with high proficiency
- indigenous energy sources cover just 1/3 of the energy demand
- CO2 tax on fuels initiated earlier in the 1990s, EU-focuses to decrease CO2 outflows - 40% by 2030
Exceptional targets set by the Finnish government to expand the share of sustainable transport fuels to 40 % by 2030 and also to quit utilizing coal in energy production and to divide the utilization of imported oil for local use. Finland is the leading producer of renewable diesel in the world with an annual production capacity of 2.6 million tons and has production in Porvoo/Finland, Rotterdam, and Singapore.
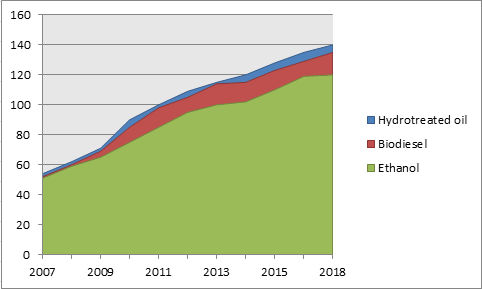
Ethanol as Biofuel:
Fuel ethanol generation has increased relentlessly in the United States since the 1980s when it was given driving force by the need to decrease energy dependence on outside provisions. The momentum has proceeded as generating costs have fallen, and as the U.S. Clean Air Act has specified a level of inexhaustible fuels to be blended with gas. The portion of yearly U.S. corn generation used to make ethanol increased from around 1 percent in 1980 to around 20 percent. and ethanol yield increased from 175 million gallons to about 5.0 billion gallons over a similar period.
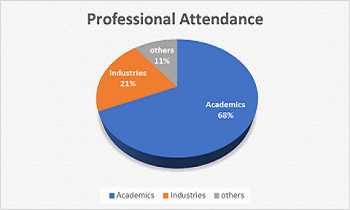
Professional attendance
Bioenergy Meet 2020 will include driving keynote speakers, session speakers, and moderators will identify demonstrating their examination on the topics related to Biofuel Scientists and Biotechnology, Chemical Engineering, Renewable Energy production and processing for Different waste products, agricultural products, and forestry products from beginning to end. Professors, researchers, Chemical-engineers, students from the field of chemical engineering, bioenergy and biofuel industries
- Academics - 68%
- Industries -21%
- Others-11%
Conference Highlights
- Feedstock and Resources for Biofuels and Biorefinery
- Biomass for Energy
- Forestry as Carbon Sink
- Environmental Impacts of Bioenergy Sector
- Bioalcohols
- Biodiesel
- Biogas
- Biomass Production and Processing
- Advanced Biofuels
- Biofuels and Renewable Energy Sector
- Drop-in Biofuels, Bio hydrocarbons
- Biorefinery
- Food vs. Fuels Debate
- Biofuels Market and Future
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | April 20-21, 2020 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Fundamentals of Renewable Energy and Applications
- Journal of Bioprocessing & Biotechniques
- Journal of Petroleum & Environmental Biotechnology
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by

















